
Bio balls have a moderately low surface area which make them one of the less efficient biomedia for submerged filters. This was confirmed by a test run on the ammonia oxidizing capability of various filter media. Bio balls did not perform very well in this test. The only good use for bioballs is as a media in trickle filters.
A Test
A test of ammonia oxidizing capability of various filter media was run. The first number, the “efficiency” is the average ammonia oxidizing that 15 cubic inches of media accomplished over a 90-day period. The second number is the “effective” surface area in square feet per cubic feet calculated from that test. The third number is the effective surface area in square feet per cubic feet calculated by simple mathematics. The correlation between the test results and the calculated surface area is very significant and means the testing was accurate.
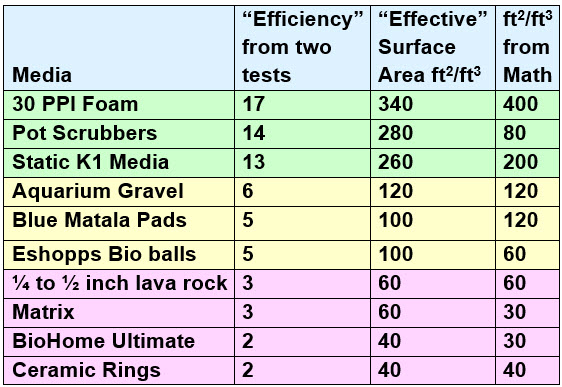
The higher the numbers here the better the media. This makes 30 ppi foam the best static media for canisters and ceramic rings the worst. Bioballs did not do too well in these two tests. But bio balls are the best media for aerating trickle filters due to the relationship between the size of the openings and the size of a drop of water.
Types of Bioballs
There are many variations on bioballs. For instance:

‘

The bioballs with an open design and cylindrical plastic surfaces are the best media for trickle filters.
One type of bioball has a hollow center filled with urethane foam. Sounds good, but since there is no pressure drop across the foam in a submerged filter, there is going to be very little flow through the foam. Which means it is just a good marketing talking point, not a true benefit.

This foam bioball media will be slightly better than straight bioballs in a trickle filter for biofiltration. The foam will adsorb water and move it though the foam as it drips onto the bioballs, which will give some added biofiltration. The foam does nothing for aeration.
Note that some bioballs have narrow slots molded in them which are less than the diameter of a drop of water (roughly 3 millimeters or 1/8 of an inch). These bioballs don’t work well in a trickle filter.
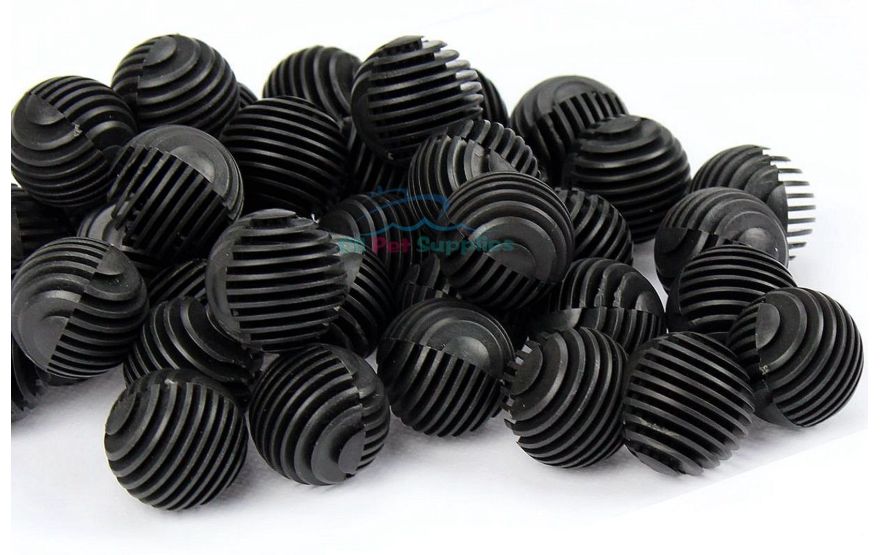

In small quantities bioballs are expensive ($15 to $40 per liter). In large quantities they are far less expensive ($3.48 for one gallon, $25 for one cubic foot or 7.5 gallons).
Note that trickle filters using bioballs have quite rightly fallen out of favor with home aquarists. Trickle filters have about 25% of the efficiency of a static submerged filter on a cubic inch to cubic inch basis.
.
Return to Filter Media Menu
Return to Media List Menu
.
Aquarium Science Website
The chapters shown below or on the right side in maroon lead to close to 400 articles on all aspects of keeping a freshwater aquarium. These articles have NO links to profit making sites and are thus unbiased in their recommendations, unlike all the for-profit sites you will find with Google. Bookmark and browse!
.

Leave a Reply